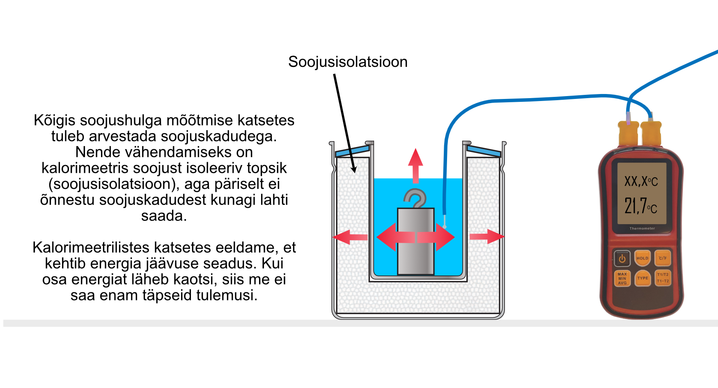
Find out how heat losses occur. Consider how to reduce them and how they affect the reliability of calorimetric experiments. Answer the question.
Heat losses are greater the faster the heat transfer, which we cannot control in the experiment. Such transfers can take place, for example, through the thermal insulation of the calorimeter, as well as during water evaporation and convection, when water comes into contact with the outside air. Better thermal insulation must be used to reduce heat loss: thicker and better material thermal insulation; the use of a lid when working with water, etc.
It is also a good idea to use water for measurements whose temperature is close to the temperature of the outside air, because the heat transfer through the vessel walls is slower when the temperature difference between the water and the outside air is small. We will also notice these things in the experiments of the next lesson (Energy and Power).