A supercapacitor is ... like a capacitor, but with a very large capacity. It can be charged, and when a charged supercapacitor is connected to a circuit, it acts as a current source.
To charge a supercapacitor, it is necessary to conduct ... charges, that is, electric current.
In the diagram below, you can also see the sign of a supercapacitor - two vertical dashes that are not connected to each other. This is also the idea of capacitors - the charges do not pass through the capacitor, but they accumulate on the surfaces inside the capacitor, positive charges on one surface, negative charges on the other.
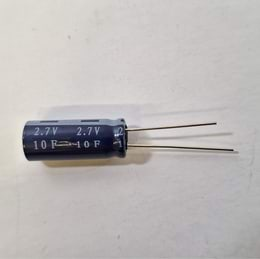
The more charges a capacitor can hold, the greater its capacity. The capacitance of a supercapacitor is very large, hence the prefix "super".
Charges accumulated in the capacitor create a voltage across the capacitor terminals. And if we stop charging and connect its terminals to a circuit, the charges will move with the support of this same voltage, an electric current will be generated.
The supercapacitor itself has become a current source.
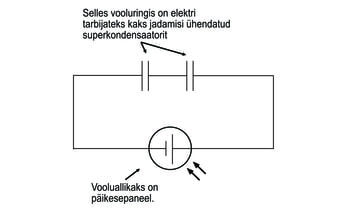
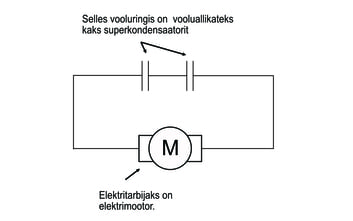
In the picture on the left, you can see the circuit diagram that can be used to charge capacitors using a battery. On the right side of the figure is a circuit diagram that allows charged capacitors to be used to start an electric motor.
We calculate the time required to charge or discharge the capacitor from the formula , which is obtained by combining the formulas and .
| Capacitance of the capacitor | F | ||
| The rated voltage of the capacitor | |||
| Current strength when charging a capacitor | |||
| The time it takes to charge or discharge a capacitor | s = | ||
Write down the test data here.
| Charging current at the beginning of the test | ||
| Charging current at the end of the test | ||
| Charging time | s | |
| Voltage on the capacitors at the end of charging |